Publications
2024
-
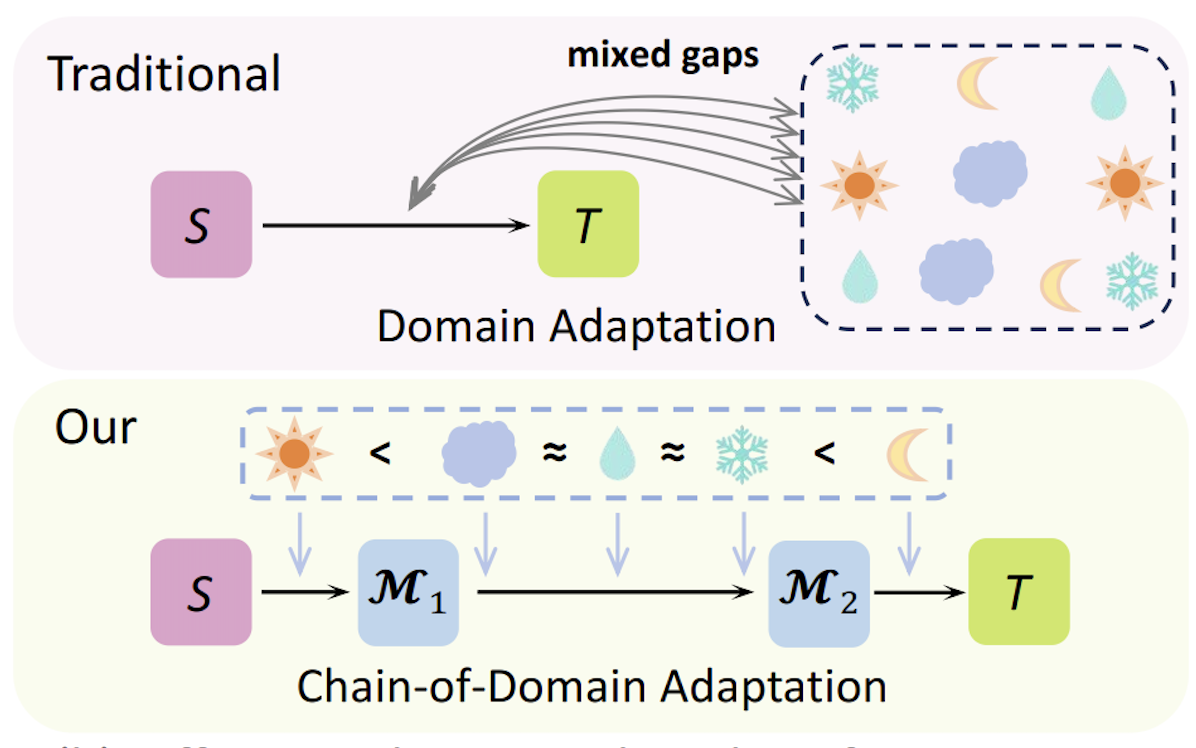 CoDA: Instructive Chain-of-Domain Adaptation with Severity-Aware Visual Prompt TuningZiyang Gong, Fuhao Li, Yupeng Deng, and 3 more authorsIn European Conference on Computer Vision, 2024
CoDA: Instructive Chain-of-Domain Adaptation with Severity-Aware Visual Prompt TuningZiyang Gong, Fuhao Li, Yupeng Deng, and 3 more authorsIn European Conference on Computer Vision, 2024Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) aims to adapt models from labeled source domains to unlabeled target domains. When adapting to adverse scenes, existing UDA methods fail to perform well due to the lack of instructions, leading their models to overlook discrepancies within all adverse scenes. To tackle this, we propose CoDA which instructs models to distinguish, focus, and learn from these discrepancies at scene and image levels. Specifically, CoDA consists of a Chain-of-Domain (CoD) strategy and a Severity-Aware Visual Prompt Tuning (SAVPT) mechanism. CoD focuses on scene-level instructions to divide all adverse scenes into easy and hard scenes, guiding models to adapt from source to easy domains with easy scene images, and then to hard domains with hard scene images, thereby laying a solid foundation for whole adaptations. Building upon this foundation, we employ SAVPT to dive into more detailed image-level instructions to boost performance. SAVPT features a novel metric Severity that divides all adverse scene images into low-severity and high-severity images. Then Severity directs visual prompts and adapters, instructing models to concentrate on unified severity features instead of scene-specific features, without adding complexity to the model architecture. CoDA achieves SOTA performances on widely-used benchmarks under all adverse scenes. Notably, CoDA outperforms the existing ones by 4.6%, and 10.3% mIoU on the Foggy Driving, and Foggy Zurich benchmarks, respectively.
-
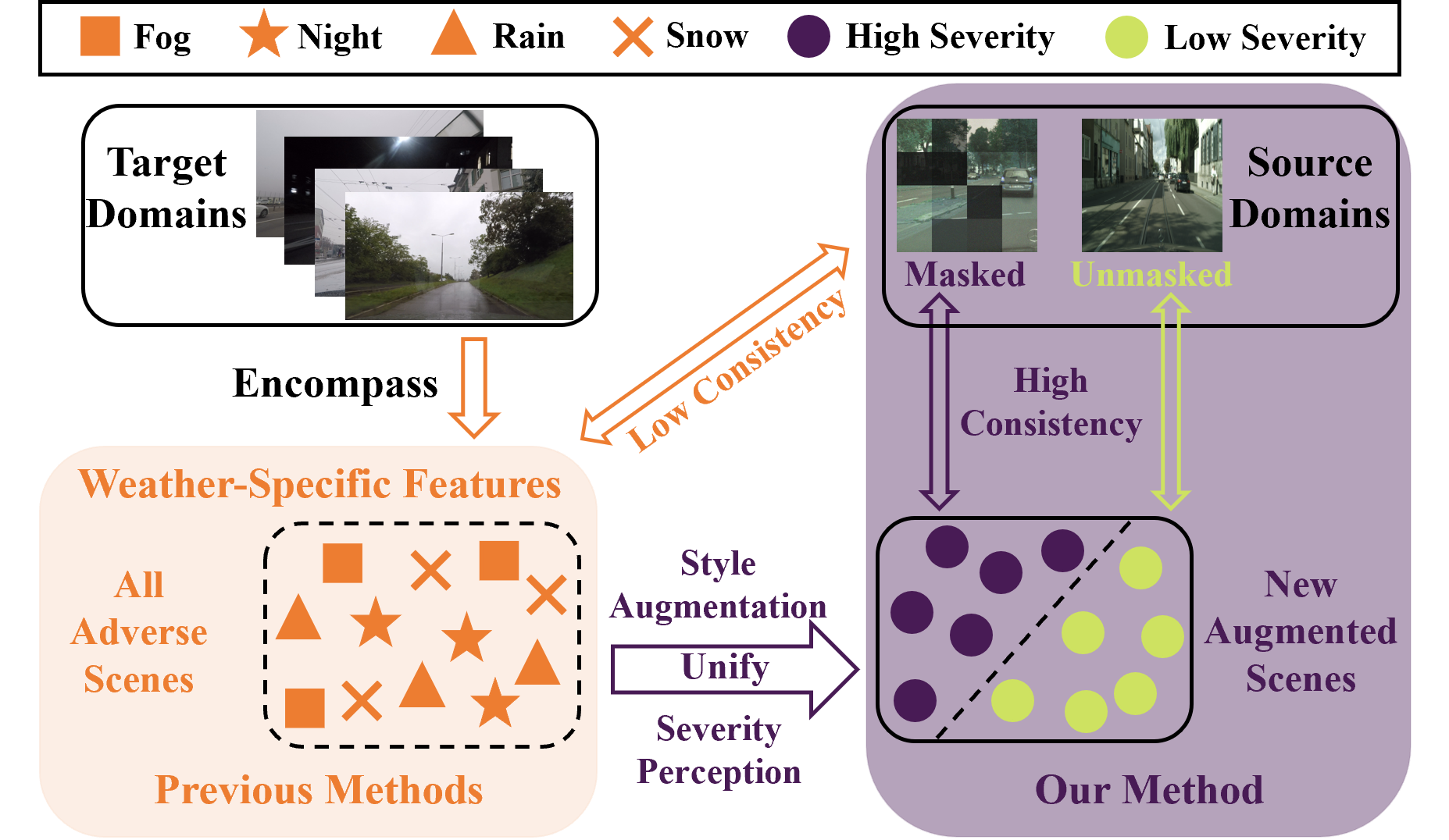 Parsing All Adverse Scenes: Severity-aware Semantic Segmentation with Mask-enhanced Cross-domain ConsistencyFuhao Li, Ziyang Gong, Yupeng Deng, and 5 more authorsIn Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2024
Parsing All Adverse Scenes: Severity-aware Semantic Segmentation with Mask-enhanced Cross-domain ConsistencyFuhao Li, Ziyang Gong, Yupeng Deng, and 5 more authorsIn Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2024Although recent methods in Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) have achieved success in segmenting rainy or snowy scenes by improving consistency, they face limitations when dealing with more challenging scenarios like foggy and night scenes. We argue that these prior methods excessively focus on weather-specific features in adverse scenes, which exacerbates the existing domain gaps. To address this issue, we propose a new metric to evaluate the severity of all adverse scenes and offer a novel perspective that enables task unification across all adverse scenarios. Our method focuses on Severity, allowing our model to learn more consistent features and facilitate domain distribution alignment, thereby alleviating domain gaps. Unlike the vague descriptions of consistency in previous methods, we introduce Cross-domain Consistency, which is quantified using the Structure Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) to measure the distance between the source and target domains. Specifically, our unified model consists of two key modules: the Merging Style Augmentation Module (MSA) and the Severity Perception Mask Module (SPM). The MSA module transforms all adverse scenes into augmented scenes, effectively eliminating weather-specific features and enhancing Cross-domain Consistency. The SPM module incorporates a Severity Perception mechanism, guiding a Mask operation that enables our model to learn highly consistent features from the augmented scenes. Our unified framework, named PASS (Parsing All adverSe Scenes), achieves significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods on widely-used benchmarks for all adverse scenes. Notably, the performance of PASS is superior to Semi-Unified models and even surpasses weather-specific models.
2023
-
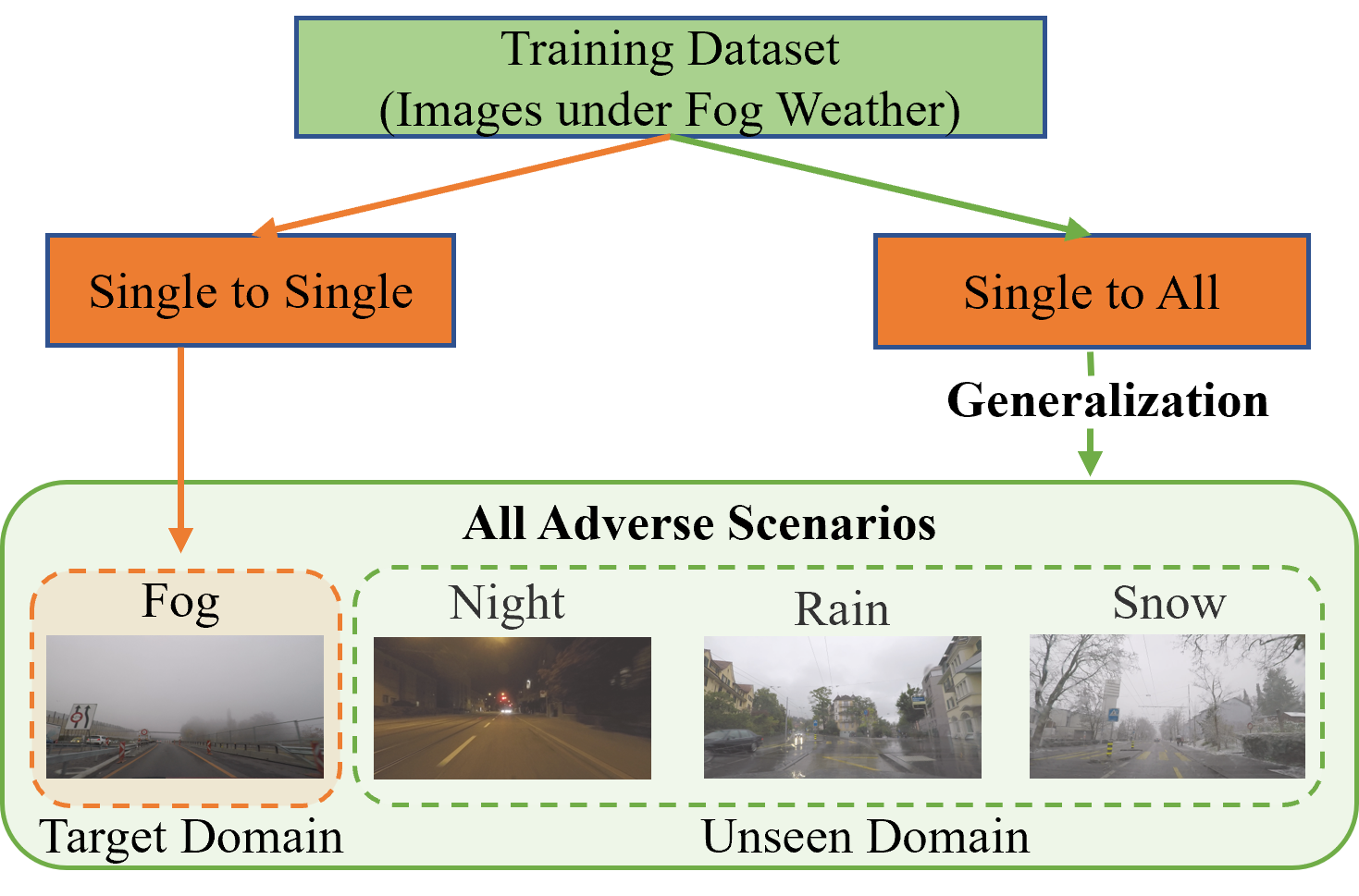 Train One, Generalize to All: Generalizable Semantic Segmentation from Single-Scene to All Adverse ScenesZiyang Gong, Fuhao Li, Yupeng Deng, and 4 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2023
Train One, Generalize to All: Generalizable Semantic Segmentation from Single-Scene to All Adverse ScenesZiyang Gong, Fuhao Li, Yupeng Deng, and 4 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2023Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) for semantic segmentation has received widespread attention for its ability to transfer knowledge from the source to target domains without a high demand for annotations. However, semantic segmentation under adverse conditions still poses significant challenges for autonomous driving, as bad weather observation data may introduce unforeseeable problems. Although previous UDA works are devoted to adverse scene tasks, their adaptation process is redundant. For instance, unlabeled snow scene training data is a must for the model to achieve fair segmentation performance in snowy scenarios. We propose calling this type of adaptation process the Single to Single (STS) strategy. Clearly, STS is time-consuming and may show weaknesses in some comprehensive scenes, such as a night scene of sleet. Motivated by the concept of Domain Generalization (DG), we propose the Single to All (STA) model. Unlike DG, which trains models on one or multiple source domains without target domains, the STA model is based on UDA and employs one source domain, one target domain, and one introduced domain to achieve generalization to all adverse conditions by training on a single-scene dataset. Specifically, the STA model is advantageous as it learns from the source domain, reserves the style factors via a Reservation domain, and adapts the unified factors by the Randomization module. An Output Space Refusion module is also further incorporated to strengthen STA. Our STA achieves state-of-the-art performance in the Foggy Driving benchmark and demonstrates great domain generalizability in all conditions of the ACDC and Foggy Zurich benchmarks.